Related links
Front-End Scripting
CMS - Content Management & Web API services
Task, Project, Quality
Task & Task pattern
System Management (part of framework)
HR - Human Resources
Mobile & Web Application
- clientprogramming_fevaldataobject
- userinterface-objectstructure
- cliplink
- npmlibraries
- fclip
- drag-drop
- AyMINE Application
- objectdefinition_inlineedit
- npmlibraries_stringlibrary
- clientprogramming
- mobileapplication
- languagesupport
- objectdefinition_multiupdate
- clientprogramming_fevalglobal
- clientprogramming_fevallanguage
- clientprogramming_fevaluser
- objectdefinition_viewdefinition
- offlineobjects
- System console
- Runtime debugging
- objectdefinition_detailview
Framework Core functionality
- prices
- managementfaq
- prices_private-installation
- clientdefinedattributes
- phplibraries
- servermethods
- io_export
- AyMINE Framework Server
- The AyMINE licence model
- System Rights
- servermethods_frmfrm
- io_import
- multiclient-architecture
- servermethods_stringsandtranslations
- frmevent
- System messaging
- usersessions
- User defined fields
Libraries & Lincences
Module - support for management
FI - Finance Management
Sales & Asset management
Sales related services
Description of a part of the AM module - sales partEncrypted shared data vault and key wallet
- Enycrypted vaults – busienss analysis
- How behaves the vaults
- How wallet behaves
- Information stored in the vault
- How encryption affects work with object
- Protection of data at the server side
Encrypted vault provide 100% encrypted information storage secured by E2E encryption
System support 100% secure storage of data vaults encrypted at users' local computer. However, system support sharing encrypted data with persons who get a key and password from you,
Enycrypted vaults – busienss analysis
The following picture is a global overview of the functionality related with the vault encryption, key and user management:
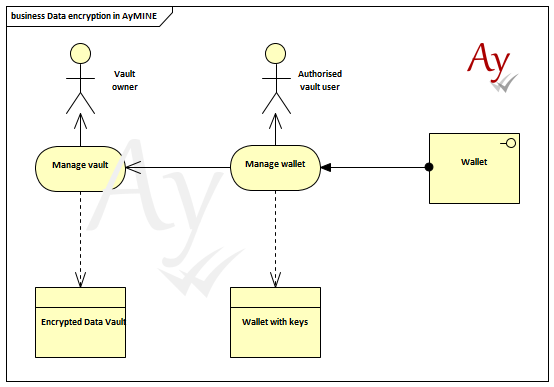
The next two images provides 2nd step of the busienss analysis – overview of the principal processes
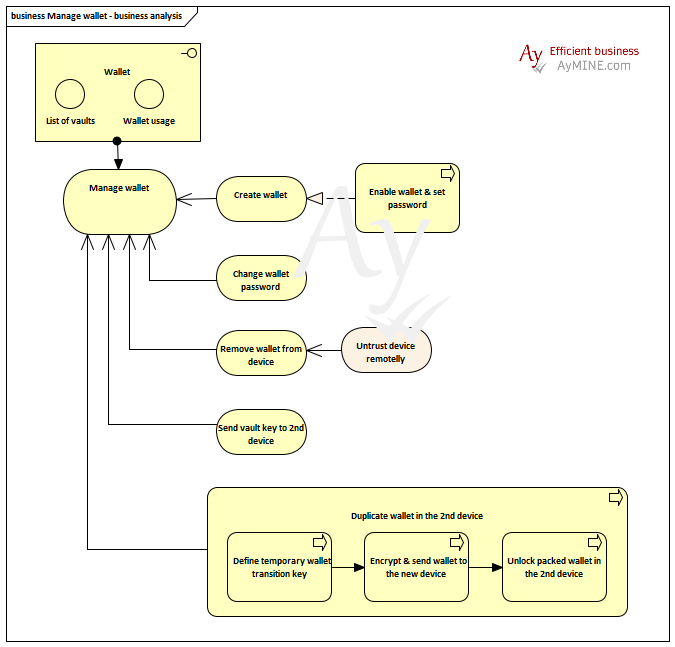
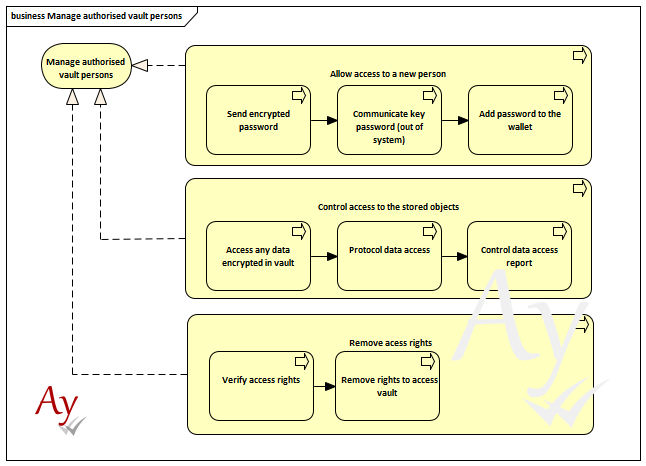
How behaves the vaults
Each user could create as many vaults as necessary. Each vault has its own system-generated long password and uses AES encryption at the local computer or mobile device.
User creates vaults and the password is encrypted by master password known only by the vault owner. He might enable the access to the vault to anybody else but new person should get:
- invitation with encrypted key for the vault
- password that allows access to the encrypted key. System stores information how has access to the vault and who provided the access.
System has no access to the data in the vault and could never unlock data that are once locked by authors. However, each owner of the key could enable that.
How wallet behaves
User uses the wallet to store the keys
How the keys are managed
Each user has its own wallet with all keys stored in local computer. Wallet is always encrypted and only the owner knows the password. Neither system nor anybody else could ever unlock the wallet. The keys for wallet is never stored by the system, but the encrypted wallet could be transferred between user's devices and preserve in case that user loose the device.
Information stored in the vault
Any object could be stored in single vault. The object stored in the vault is encrypted by the vault key. Each object that support encryption, should define attributes that are encrypted. Vault encrypts data stored in fields with the field attribute vEncrypt Remember, that encrypted content is larger than the original and the field should support larger content. E.g. system attributes could hardly be encrypted because two letter space and the possibility to estimate the value makes encryption for counter unusable.
How encryption affects work with object
Searching
The most important change is that encrypted fields do not support searching. Search is made by server and that cannot access the content and access in that
Ordering
From the same reason as searching, encrypted field cannot be used for ordering items.
Speed
Objects are temporarily encrypted by client. Values are not stored and so each time user reads encrypted values (e.g. reloaded a list with them), values are newly decrypted. It definitely hinders the processing and system is lowlier with encrypted items.
Protection of data at the server side
User Wallet with keys
Wallet is saved in the system but its security is not threatened. Keys are double-secured by the long password. It is encrypted by the long password stored at the local user devices. Access to the long password is user-password or fingerprint controlled. User can only access the keys in the wallet if (s)he unlock the password that is used to unlock password to the individual vaults
Vaults protection
Each vault has unique password but the password is not known to the users. The password is stored in the wallet and encrypted and used at the local computer when requested. User never use them directly.
Password to the vaults are always at least 40 characters long, system-generated and never stored unprotected.